강의 요약 - CS224n: Natural Language Processing with Deep Learning (4)
30 Aug 2022
Reading time ~5 minutes
I. Contents
- Machine translation
- Seq2seq
- Neural Machine Translation
- Training a Neural Machine Translation System
- Multi-layer RNNs
- Decoding varieties
- Evaluating Maching Translation
- Attention
- Seq2seq: the bottleneck problem
- Attention
II. Machine Translation
Machine Translation is the task of translating a sentence \(x\) from one language (the source language) to a sentence \(y\) in another language (the target language).
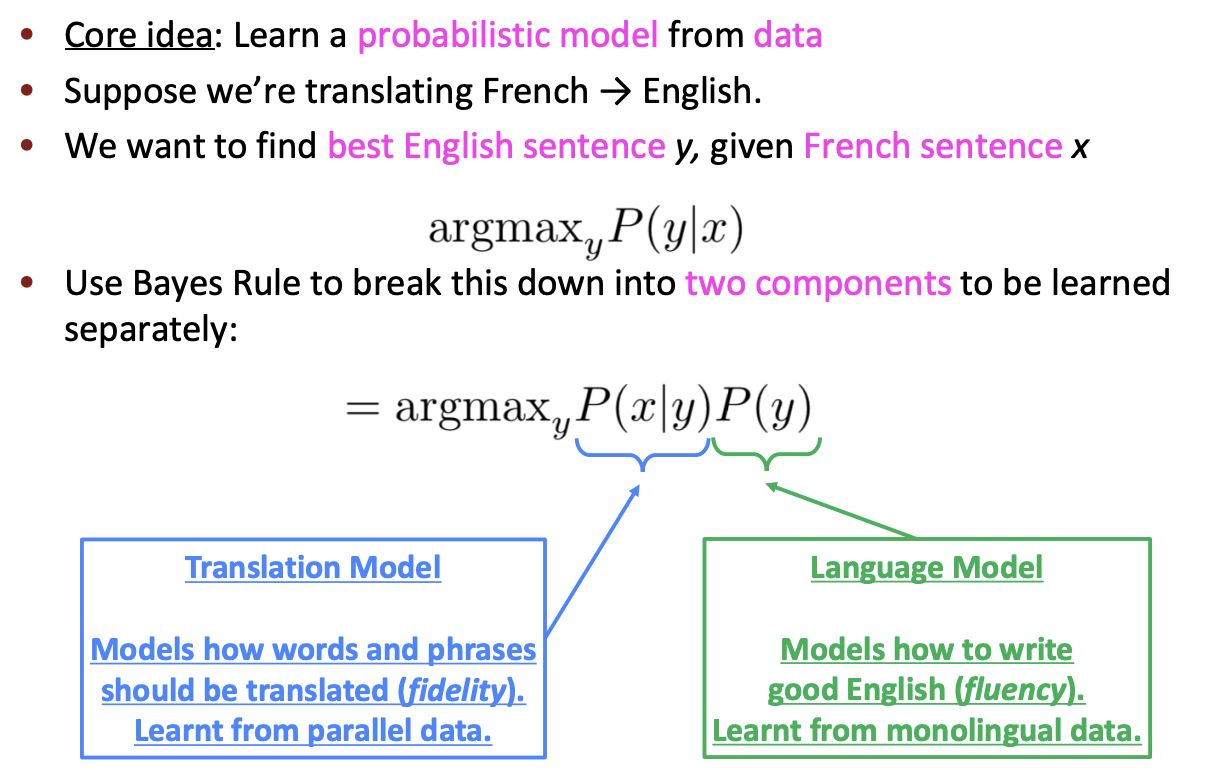
1990s-2010s: Statistical Machine Translation
Alignment
- Q. How to learn translation model \(P(x\mid y)\)?
- First, need large amount of parallel data e.g. The Rosetta Stone
- Break it down further: Introduce latent \(a\) variable into the model: \(P(x, a\mid y)\) where \(a\) is the alignment, i.e. word-level correspondence between source sentence \(x\) and target sentence \(y\)
- Alignments are latent variables: They aren’t explicitly specified in the data!
언어마다 문법이나 단어 체계가 다르기 때문에, 번역을 하기 위해서는 source sentence와 target sentence 의 단어가 각각 어떻게 대응되는지 파악해야하며, 이를 alignment라고 한다.
Alignment는 one-to-one, many-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-many 등 복잡하게 구성되며, dependency parsing에서의 arc처럼 명시적으로 특정되지 않고 SMT에 내장되므로 latent variable이라고 부른다.
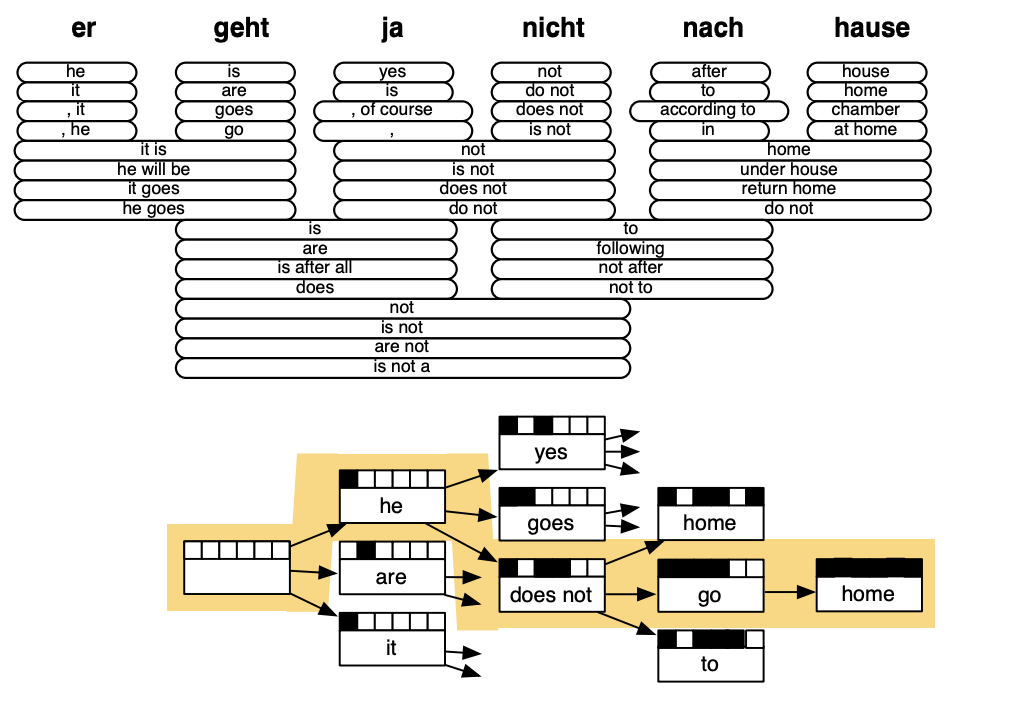
Decoding for SMT
Enumerating every possible \(y\) and calculate the probability is too expensive.
Answer : Impose strong independence assumptions in model, use dynamic programming for globally optimal solutions
Conclusion
The best systems of SMT were “extremely complex”
III. Seq2Seq
1. Neural Machine translation
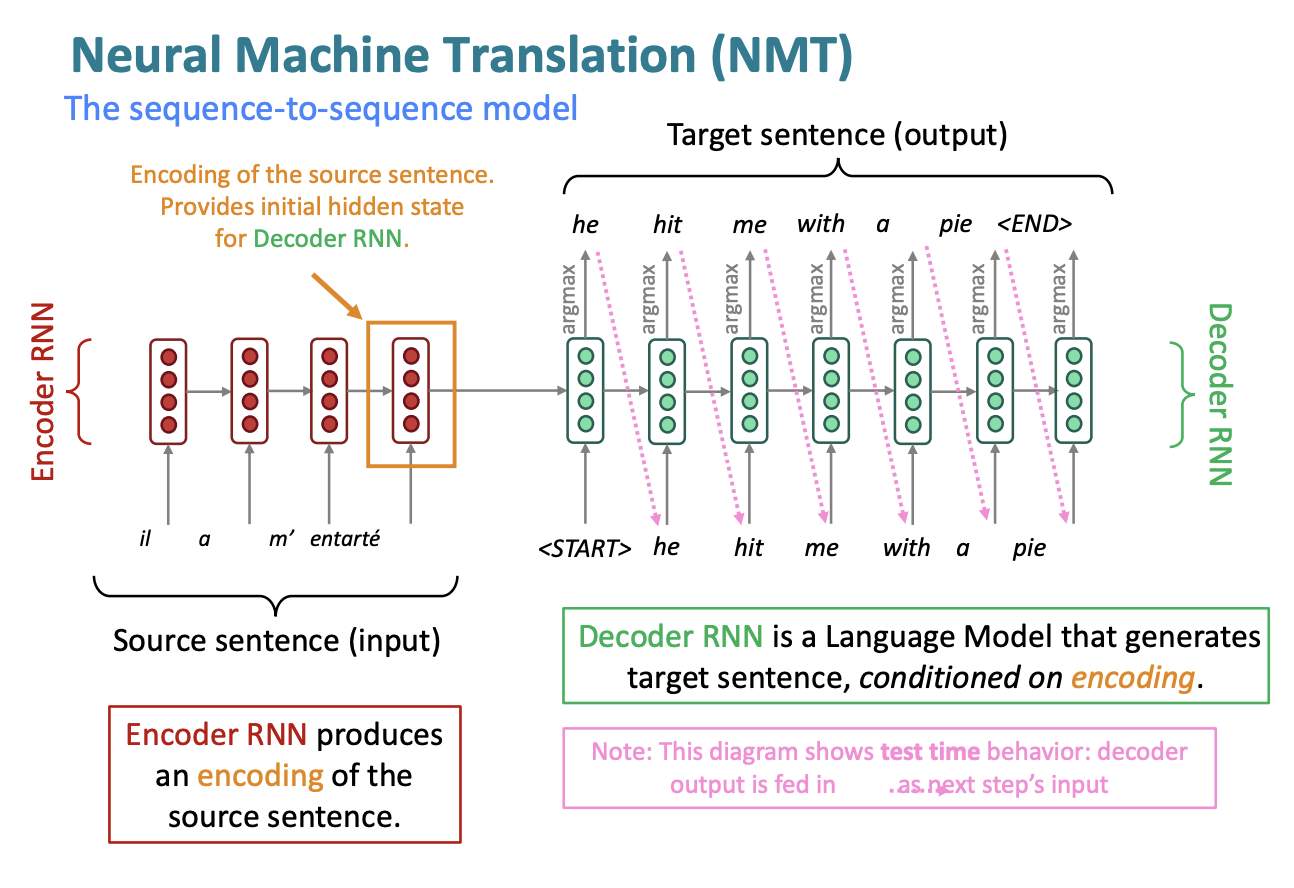
Neural Machine Translation (NMT) is a way to do Machine Translation with a single end-to-end neural network
The neural network architecture is called a sequence-to-sequence model (a.k.a. seq2seq) and it involves two RNNs
- seq2seq is useful for more than just MT
- Summarization
- Dialogue
- Parsing
- Code generation
- seq2seq model is an example of a Conditional Language Model
2. Training a Neural Machine Translation System
\[J(\theta) = \frac {1}{T} \sum_{t=1}^T J_t\] (\(J_t\) is negative lof prob of the word)
seqseq is optimized as a single system, Backpropagation operates “end-to-end”
3. Multi-layer RNNs
- High-performing RNNs are usually multi-layer : 2 to 4 layers!
- Usually, skip-connections/dense-connections are needed to train deeper RNNs (e.g. 8 layers)
- Transformer-based networks (e.g. BERT) are usually deeper, like 12 or 24 layers.
4. Decoding varieties
Greedy Decoding
- Take most probable word on each step
- Greedy decoding has no way to undo decisions
Exhaustive search Decoding
- Ideally : We could tru computing all possible sequences \(y\) and find \(y\) that maximizes : \[P(y\mid x)=\prod^T_{t=1}P(y_t\mid y_1,\cdots ,y_{t-1},x)\]
- This \(O(V^T)\) complexity is far too expensive!!!
Beam search Decoding
- Core idea : On each step of decoder, keep track of the k most probable partial translations (which we call hypotheses)
- Beam search is not guaranteed to find optimal solution, but much more efficient than exhaustive search.
Advantages and Disadvantages of NMT
Advantages
- Better performance
- A single neural network to be optimized end-to-end
- No subcomponents to be individually optimized
- Requires much less human engineering effort
- No feature engineering
- Same method for all language pairs
Disadvantages
Compared to SMT :
- Less interpretable
- Difficult to control (e.g. can’t easily specify rules or guidelines for translation)
5. Evaluating Maching Translation
BLEU (Bilingual Evaluation Understudy)
BLEU compares the machine-written translation to one or several human-written translation(s), and computes a similarity score based on :
- n-gram precision
- Plus a penalty for too-short system translations
Learn More - Incredible.AI : BLEU
- BLEU is useful, but imperfect
IV. Attention
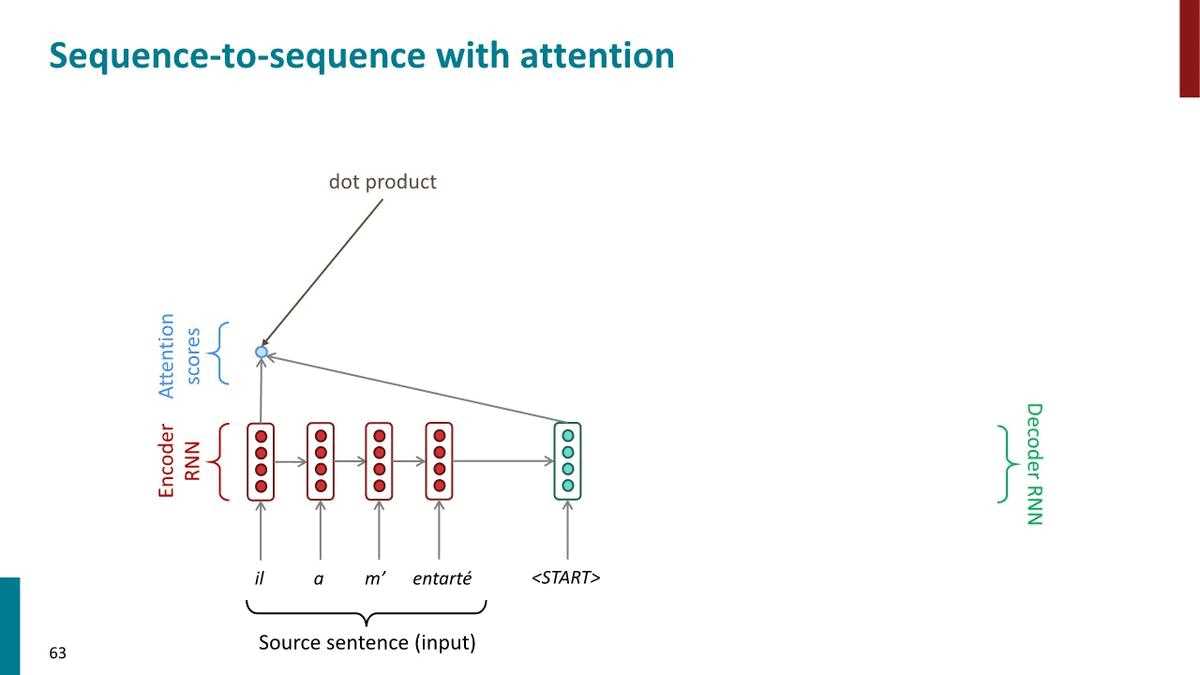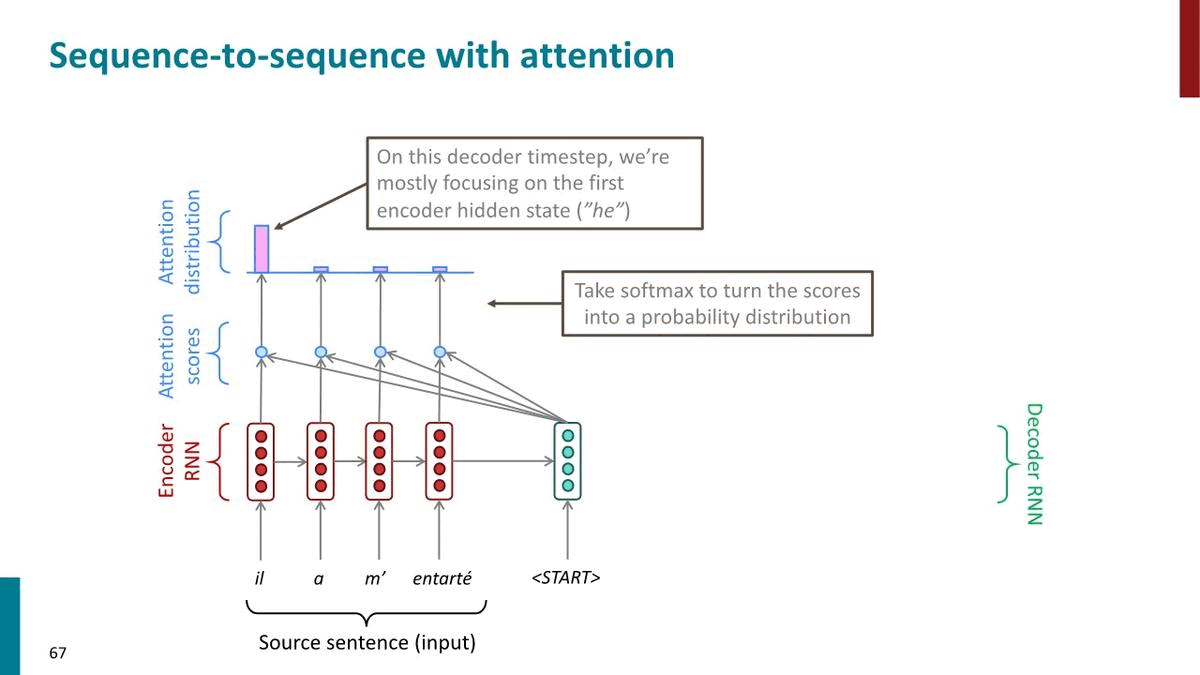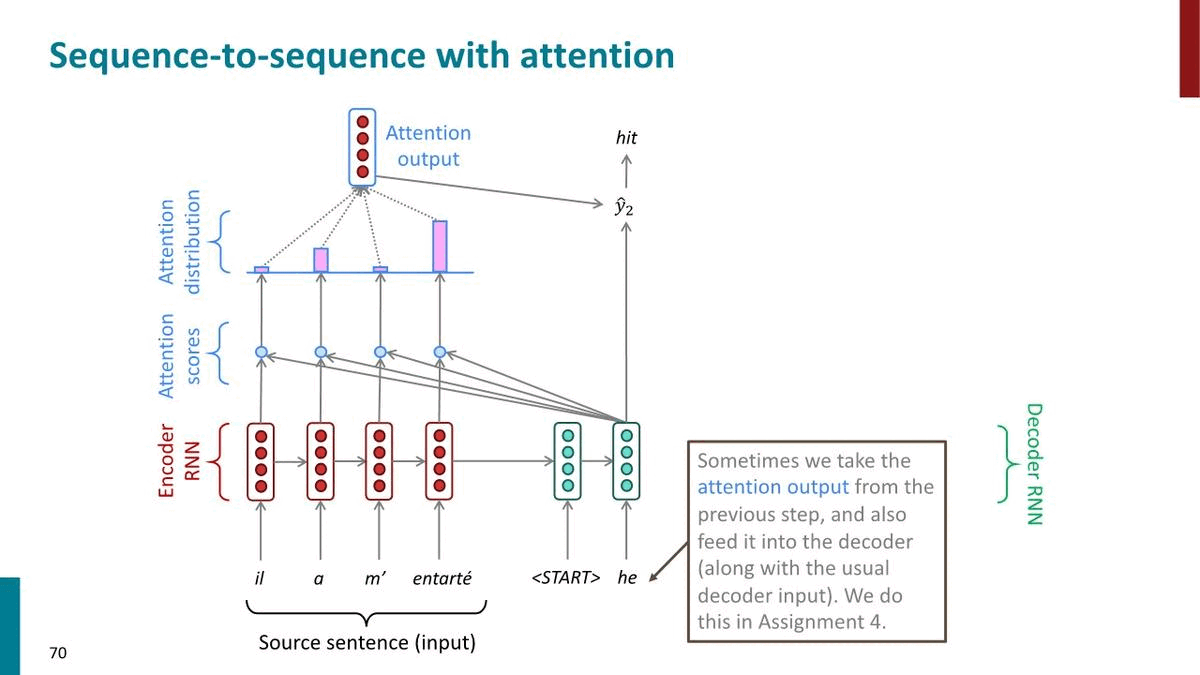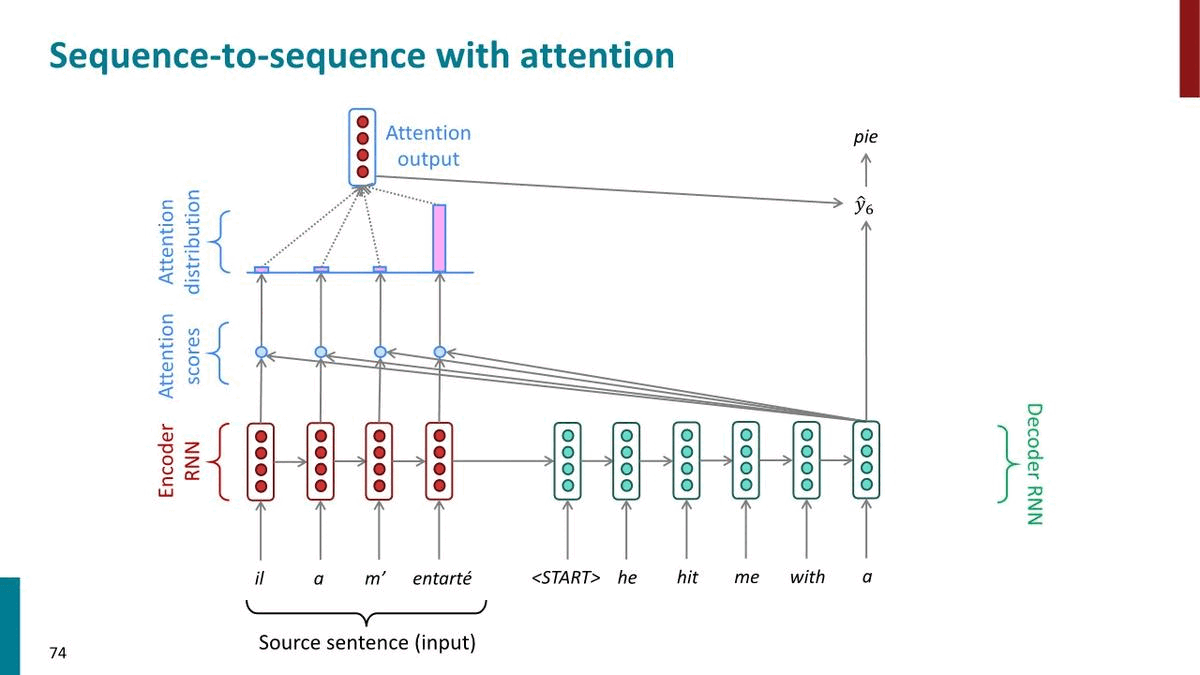
1. Seq2seq: the bottleneck problem
The last hidden state of encoder which is fed to decoder needs to capture all information about toe source sentence. ☞ “Information Bottleneck!”
2. Attention
Overview
Attention provides a solution to the bottleneck problem
Core idea: on each step of the decoder, user direct connection to the encoder to focus on a particular part of the source sequence
실제로 사람이 번역을 할 때에도, source sentence를 읽고 곧바로 target sentence를 써내려가기보다는 target sentence를 작성하면서 source sentence를 다시 읽어보기도 하고, 계속 시선이 왔다갔다 한다. 이러한 컨셉을 direct connection으로 구현한 것이 Attention이다.
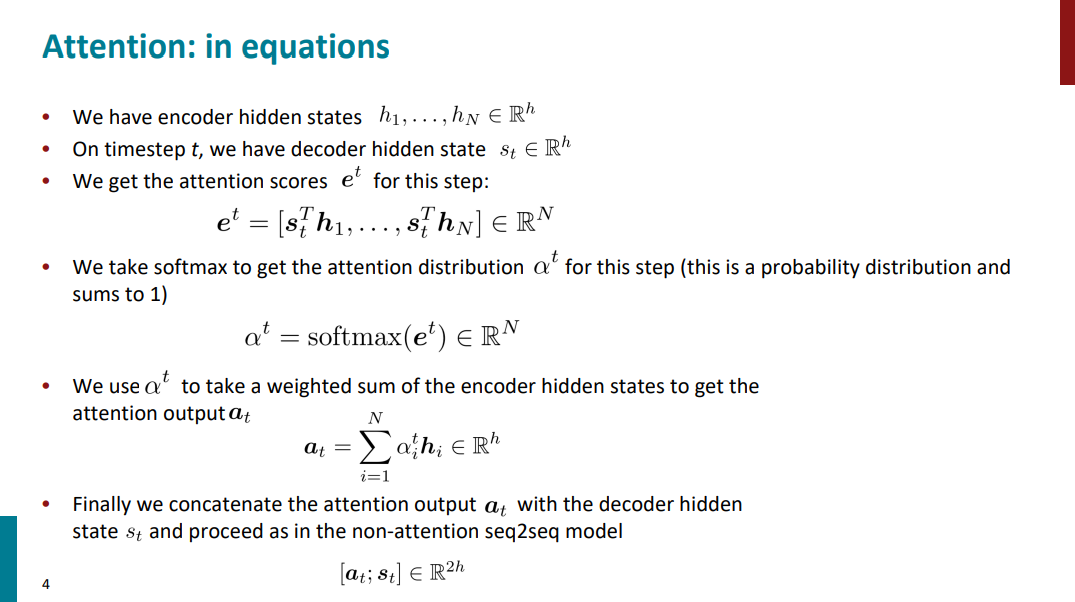
Attention in equations
CS224n Assignment 4 Handout : Attention with Bidirectional LSTMs

Attention is great!
- Attention significantly improves NMP performance
- Attention solves the bottleneck problem
- Attention helps with vanishing gradient problem
- Attention provides some interpretability
- By inspecting attention distribution, we can get (soft) alignment for free!
- The network just learned alignment by itself
Attention is a general Deep Learning technique
- You can use attention in “many architectures” (not just seq2seq) and “many tasks” (not just MT)
- More general definition of Attention
Given a set of vector values, and a vector query, attention is a technique to compute a weighted sum of the values, dependent on the query
- We somtimes say that the “query attends to the values.”
- e.g. in the seq2seq + attention model, each decoder hidden state (query) attends to all the encoder hiddent states (values).
StackExchange : What exactly are keys, queries, and values in attention mechanisms?
Attention에서 말하는 key, query, 그리고 value가 무엇인지 선뜻 이해되기 어렵다. 위 StackExchange 답변에 자세히 설명되어있으며, 이해한 바를 옮기자면 다음과 같다.
일단, key, query, value는 Retrieval System에서 통용되는 개념이다. 가령 유튜브에서 영상을 검색한다고 하면, 각각 아래와 같은 의미를 가진다.
The key/value/query concept is analogous to retrieval systems. For example, when you search for videos on Youtube, the search engine will map your query (text in the search bar) against a set of keys (video title, description, etc.) associated with candidate videos in their database, then present you the best matched videos (values).
그리고 Attention model에서 어떤 값이 각각 key, query, value에 대응되는지 알아야 그 다음을 이해할 수 있다.
- key는 첫번째 식에서의 \(h_1,\cdots ,h_N\)
- query는 첫번째 식에서의 \(s_t\)
- value는 세번째 식에서의 \(h_i\)에 대응된다.
우선, Attention이란 무엇인가? 바로 각 step마다 source sentence 중 어떤 부분에 “attention”을 두고 단어를 생성(if MT)할지 결정하는 것이다. \(\alpha^t\)를 가중치로 value들의 weighted sum을 계산한다는 말은, 큰 가중치를 갖는 부분에 큰 “attention”을 둔다는 것을 의미한다.
\(\alpha^t\)를 softmax가 아닌 one-hot vector라고 생각하면 더욱 명확해진다. one-hot vector라면 encoder가 생성한 수개의 hidden state (value) 중 단 하나만 골라서 이 부분에’만’ attention을 두고 decoding을 하게되는 것이다. 더 나아가, one-hot vector의 마지막 원소가 1이라면 이는 Simple seq2seq과 동치임을 알 수 있다.
그렇다면 다시 key, query, value의 개념으로 돌아가서, 왜 key와 query의 내적값으로 가중치 \(\alpha^t\)를 구하는걸까? 위의 유튜브 검색 비유를 통해 보자면, key를 query에 mapping하여 그 값을 토대로 value를 산출한다. Attention에서는 key와 value를 mapping하는 방법으로 벡터간의 내적을 채택하는 것이다.
Decoder의 매 Step마다 query (\(s_t\))는 매번 바뀌고, key (\(h_1,\cdots ,h_N\))는 고정된 값임을 되짚어본다면 왜 key와 query인지 이해할 수 있을 것이다.
Attention variants
\(\alpha^t = softmax(e^t)\) 에서 \(e^t\) 를 계산하는 방법으로 dot-product만 논했으나, 여러가지 방법이 더 있다.
- Basic dott-product attention: \[e_i=s^Th_i\in \mathbb{R} \]
- Multiplicative attention \[e_i=s^TWh_i\in \mathbb{R} \]
- Reduced rank multiplicative attention \[e_i=s^T(U^TV)h_i=(Us)^T(Vh_i)\in \mathbb{R} \]
- Additive attention \[e_i=v^Ttanh(W_1h_i+W_2s) \in \mathbb{R} \]