강의 요약 - CS224n: Natural Language Processing with Deep Learning (1)
27 Aug 2022
Reading time ~4 minutes
I. Contents
- Human language and word meaning
- How do we represent the meaning of a word?
- Word2Vec
- GloVe
- Summary
II. Human language and word meaning
1. How do we represent the meaning of a word?
(1) Definition : meaning
Webster 영영사전 : the idea that is represented by a word, phrase, etc.
표준국어대사전(“의미”) : 말이나 글의 뜻
(2) Commonest linguistic way of thinking of meaning :
\[signifier(symbol) ↔ signified(idea or thing)\]
(3) Common NLP solution
WordNet, a thesaurus containing lists of synonym sets and hypernyms
동의어, 유의어(synonyms) 또는 상의어(hypernyms)로 이루어진 사전을 통해 의미를 정의할 수 있다.
※ WordNet의 문제점
- 뉘앙스를 담을 수 없다.
- 단어의 새로운 의미를 담을 수 없다.
- 동의어 등을 판단하는 기준이 주관적이다.
- 제작하는데 인력이 많이 소모된다.
- Word Similarity를 계산할 수 없다.
(4) Representing words as discrete symbols
“One-hot vector” representing : \[motel = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0] \ hotel = [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0]\]
※ One-hot vector representing의 문제점 모든 vector들이 orthogonal하기 때문에, similarity를 계산할 수 없다.
(5) Representing words by their context
Distributional semantics : A word’s meaning is given by the words that frequency appear close-by. When a word \(w\) appears in a textm its context is the set of words that appears nearby.
특정 단어의 의미는, 글에서 그 특정 단어 주변에 어떤 단어들(=context)이 주로 오는지에 따라 파악할 수 있다. 위 아이디어를 이용하여, 단어를 Vectorize 할 수 있다.
Note : Word vectors are also called word embeddings or word representations, They are a distributed representation.
(6) Conclusion
NLP에서 단어를 표현하는 방식으로 WordNet, discrete representations, distributed representation 등이 있다. 이때 NLP에서 “유용한” 방식으로 단어를 표현하기 위해서는, 단어 간 유사도(Similarity)를 계산할 수 있도록 distributed representation이 가장 적절한 해법이다. Distributional semantics에서 착안하여, 단어들을 실수 벡터로 표현하는 방법으로 Word2Vec을 알아본다.
2. Word2Vec
(1) What is Word2Vec?
Word2Vec (Mikolov et al. 2013, PDF) is a framework for learning word vectors.
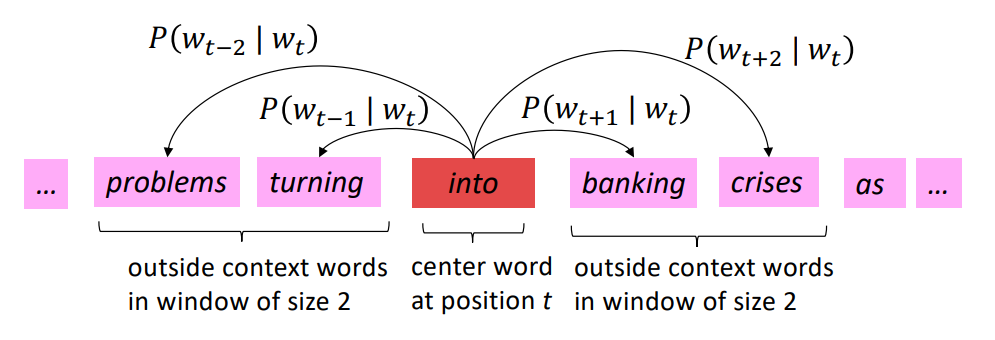
\[Likelihood = L(\theta) = \prod_{t=1}^{T} \prod_{-m \le j\le m, j\ne0} P(w_{t+j}|w_t;\theta)\] \[objective function = J(\theta) = -\frac{1}{T}log(L(\theta))\]
특정 단어에 대하여, 주변(Window)에 다른 단어들이 나타날 확률의 곱 (첫번째 \(\prod\))을 모든 단어마다 계산해 곱해주면 (두번째 \(\prod\)), 이를 Likelihood라고 하며, -Log를 취하여 objective function을 최소화 함으로써 word representation을 찾을 수 있다.
Likelihood란?
관측 데이터 \(x\)가 있을 때, 어떤 분포 \(\theta\)를 주고, 그 분포에서 데이터가 나왔울 확률을 말한다. \[L(\theta|x)=P_{\theta}(X=x)=\prod_{k=1}^n P(x_k|\theta)\] Word2Vec에서 \(\theta\)란 “to be defined in terms of our vectors”, 즉 optimze할 word vector들의 값을 의미하며(이에 따라 분포가 정해진다), 위 Likelihood의 정의로부터 본다면, \(w_t\)마다 likelihood를 구한 후 T번 곱하는 것이라고 볼 수 있겠다.
(2) How to calculate the probability?
\[P(o|c) = \frac{exp(u_o^Tv_c)}{\sum_{w\in V}exp(u_w^Tv_c)}\] This is an example of the softmax function. The softmax fuction maps arbitrary values \(x_i\) to a probability distribution \(p_i\) (“max” because amplifies probability to smaller \(x_i\), “soft” because still assigns some probability to smaller \(x_i\))
(3) Optimization
Gradient descent, chain rule, SGD … (생략)
(4) Word2Vec : More details
- Two model variants
- Skip-grams (SG) ☞ 위에서 한 내용
- Continuous Bag of Words (CBOW)
- Additional efficiency in Training
- Naive softmax
- Negative samlping
(5) The skip-gram model with negative sampling PDF
Main idea : train binary logistic regressions for a true pair(center word and a word in its context window) versus several noise pairs (the center word paired with a random word)
Likelihood를 계산하는 식 중, softmax는 computationally expensive하므로(vocabulary에 있는 모든 단어에 대해 내적 필요), 이를 Negative-sampling을 이용한 방식으로 대체한다.
3. GloVe
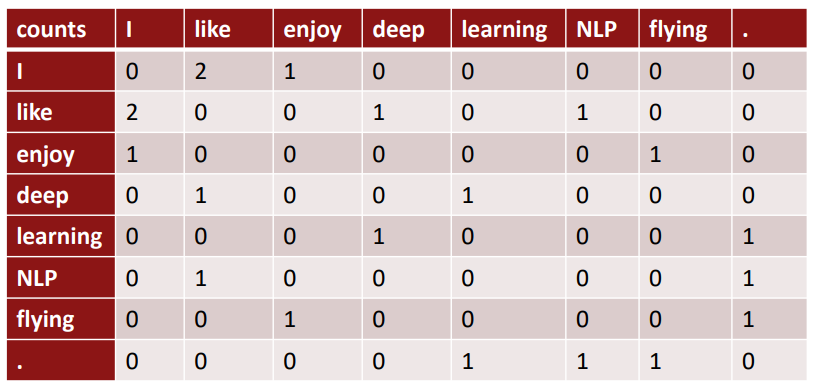
(1) Co-occurrence matrix K
- Window length 1 (most common : 5-10)
- [“I like deep learning”, “I like NLP”, “I enjoy flying”]
Co-occurrence matrix는 V * V 크기의 행렬이고, sparsity issue가 있으므로 차원을 낮추는 과정이 필요하며, 대표적으로 SVD(Singular Value Decomposition)이 있다.
이때, raw counts에 SVD를 바로 적용하는 것은 잘 작동하지 않고, the, he, has와 같이 과도하게 자주 등장하는 단어들(function words)의 count를 clipping하거나, count에 log를 취하거나, function words를 무시하는 방법 등을 추가로 요한다.
(2) GloVe
GloVe: Global Vectors for Word Representation
Q: How to we capture ratios of co-occurrence probabilities as linear meaning components in a word vector space?
A: Log-bilinear model (아래는 with vector differences) \[w_i\cdot w_j=logP(i|j) \ w_x\cdot (w_a-w_b) = log {\frac{P(x|a)}{P(x|b)}}\]
| \(w_i\cdot w_j=logP(i | j)\) 가 되도록 \(w\)를 optimize하는 것이 목표이다. \(P\)는 co-occurrence matrix로 부터 계산됨. |
\[J = \sum^V_{i,j=1}f(X_{ij})(w_i^T\tilde w_j+b_i+\tilde b_j - logX_{ij})^2\]
\(f\) -> clipping function fot function words
- Fast training
- Scalable to huge corpora
- Good performance even with small corpus and small vectors
(3) Evaluation of word vectors
Related to general evaluation in NLP : Intrinsic vs. extrinsic
Intrinsic word vector evaluation
- Word vector analogies (ex. man : woman = king : ???, ??? = queen)
- Word vector distances and their correlation with human judgements
Extrinsic word vector evaluation
- Named entity recognition
(4) Word senses and word sense ambiguity
Most words have lots of meanings!
- Improving Distributional Similarity with Lessons Learned from Word Embeddings Huang et al. 2012
- Linear Algebraic Structure of Word Senses, with Applications to Polysemy Arora et al. 2018
III. Summary
Human language를 컴퓨터가 이해할 수 있도록 표현하기 위해서는 “word vector”를 설계해야한다. 이를 위한 시도들로 Word2Vec, GloVe를 알아보았다. Word2Vec은 SG 또는 CBOW로 구현할 수 있고, gradient descent를 효율적으로 하기 위해 negative sampling을 도입할 수 있다. GloVe는 co-occurrence matrix를 이용하여 word vector를 구한다.
Word vector를 만들었으면 이를 평가할 수 있어야 한다. NLP에서 평가 지표로 Intrinsic evaluation 또는 Extrinsic evaluation이 있다.